Data and analytics technologies are rapidly evolving, especially as demand for artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) capabilities evolve. However, many businesses are grappling with a disjointed web of platform and data solutions acquired over time. This significant technical debt results in ongoing data management challenges. To harness the full potential of data and accelerate time to value, organizations must modernize their data estates by consolidating tech debt into a lake-centric approach.
The most successful companies streamline collaboration across teams, uncover insights, and fuel AI-powered innovation by adopting a lake-centric approach. By consolidating, integrating, and modernizing a data estate into a central cloud-based lake, organizations can not only manage uncontrolled data growth and storage costs, but also enable data to scale with the business, maximizing innovation and gaining a critical competitive edge.
A timeline of enterprise challenges
Historically, a typical company invested in on-premises systems to build its analytics data warehouse. The on-premises architecture tightly linked storage and compute in a single system—so, if the company needed more compute or more storage, it had to grow them together instead of independently.
As the business and its workloads grew, so did the demand on the data warehouse. The company’s information technology (IT) team had the task of integrating and maintaining numerous data sources to facilitate teams in executing various workloads, ensuring they could access them repeatedly from a centralized data repository. However, harmonizing data across data sources while meeting line-of-business requirements proved difficult. Teams wanted to control their own compute resources and data, which presented unique challenges.
As a result, the company’s independent teams and departments adopted data marts to give each of them control over their own environment. While enabling the data marts alleviated resource contention among business units, it created bigger problems. The data marts introduced data duplication, data redundancy, and management of multiple pipelines—increasing costs and complexity.
To further complicate matters, companies acquired multiple technologies and solutions from various vendors based on individual department preferences. This made managing service-level agreements (SLAs), costs, administration, and security exceedingly difficult and time consuming.
To reduce the costs and complexities of the data warehouse and data mart ecosystem, the company adopted a lower-cost data lake to address the exponential increase in data generated during the big-data movement—first with Hadoop, then with the cloud.
With the addition of each new solution and technology, additional layers of complexity grew, with multiple data formats supported in larger volumes. Data duplication grew exponentially—and often without the compute performance needed to run workloads in a timely way.
By investing in new, cloud-enabled technology without a cohesive data management strategy, the business inadvertently compounded its ecosystem challenges—with no effective way to manage the growing data and compute mess. The decisions made up to this point may have been right at each point in time, but they've negatively impacted the business, causing limited access, bottlenecks, poor utilization, management difficulties, and rising costs. How does the business untangle its data and compute mess?
Taking a lake-centric modernization approach
With the explosion of AI/ML, a lake-centric modernization approach can consolidate data, compute, and technologies into one holistic, cloud environment. A cloud-native architecture enables the critical capability to separate compute and storage. In assessing data estates—the holistic ecosystems of platforms and applications—organizations can determine which systems would benefit from a refreshed consolidation approach that prioritizes AI/ML, optimizes existing applications, and addresses the data challenges built over time.
Leading organizations are increasingly replacing legacy platforms with more agile, lake-centric approaches, combining cost-effective data management and storage with powerful analytics capabilities.
Managing uncontrolled data growth
VantageCloud Lake’s cloud-native design optimizes the separation of compute and storage. Organizations can leverage a centralized, low-cost object store while deploying independent compute resources for departments that want workload isolation from shared company data.
To reduce the complexity and uncontrolled growth of multiple data systems, companies can migrate their data warehouses, marts, and lakes into a consolidated cloud environment. Teams can work from a single copy of data in an object store that eliminates data duplication and data movement. Teams can also provision and manage compute resources to increase business performance and reduce inefficiencies.
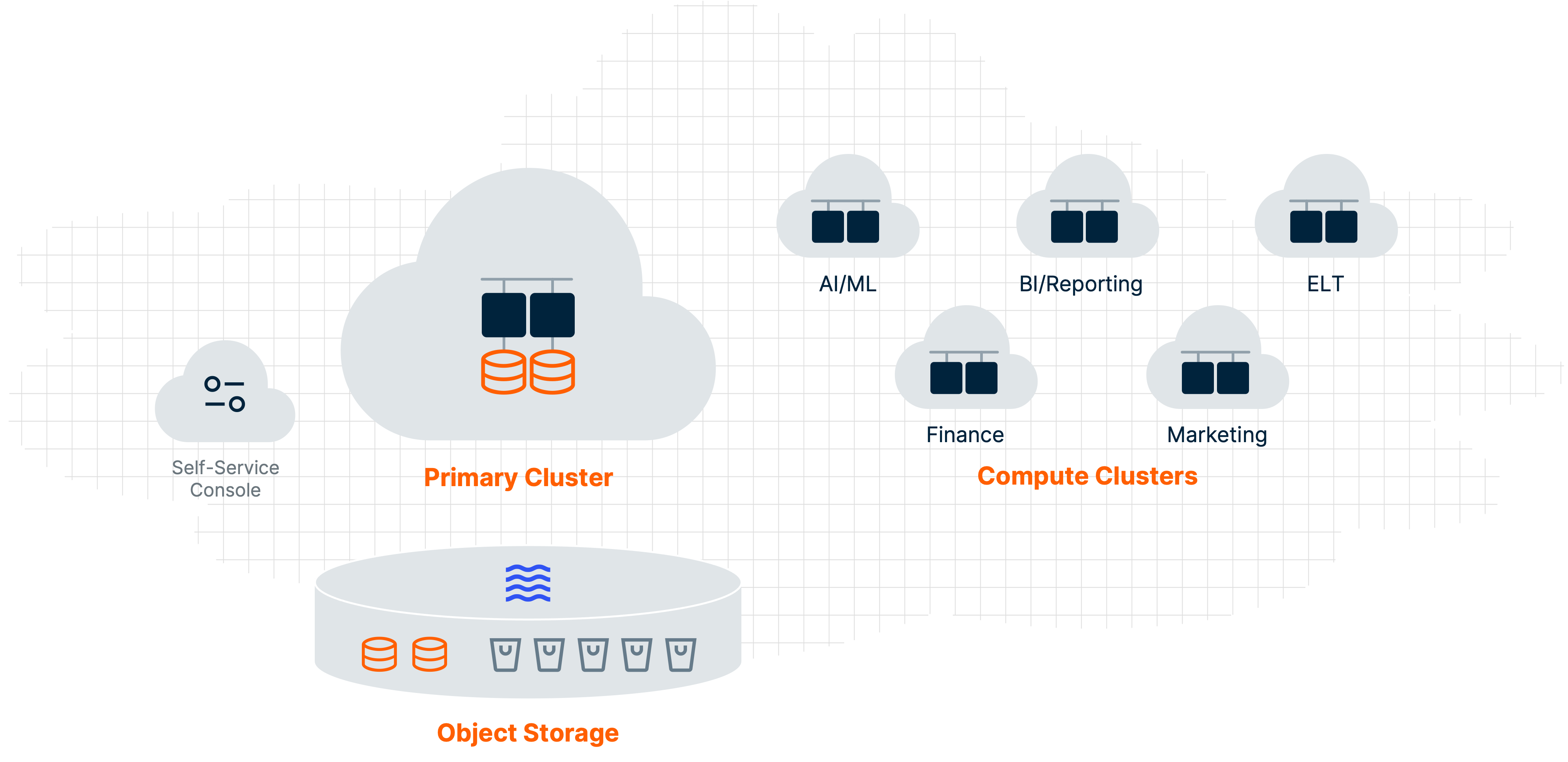
VantageCloud Lake’s architecture simplifies the process
VantageCloud Lake enables businesses to pursue lake-centric modernization. With VantageCloud Lake, enterprises can:
- Innovate faster with the ability to empower teams with multi-cluster architecture that delivers autonomy. And, with ClearScape Analytics™, Teradata’s data analytics engine included with VantageCloud Lake, teams can use industry-leading AI/ML capabilities to capture greater return on investment (ROI) and faster time to value.
- Scale smarter with dynamic resource allocation featuring extreme elasticity. VantageCloud Lake is cost-effective and environmentally sustainable, enabling “smart” scaling with business needs.
- Govern better with centralized data management and effective financial governance of cloud resources. Oversight enables teams to manage uncontrolled data growth, eliminate overruns, and provide flexibility—without impacting core operations.
Learn more about taking a lake-centric modernization approach with VantageCloud Lake.

